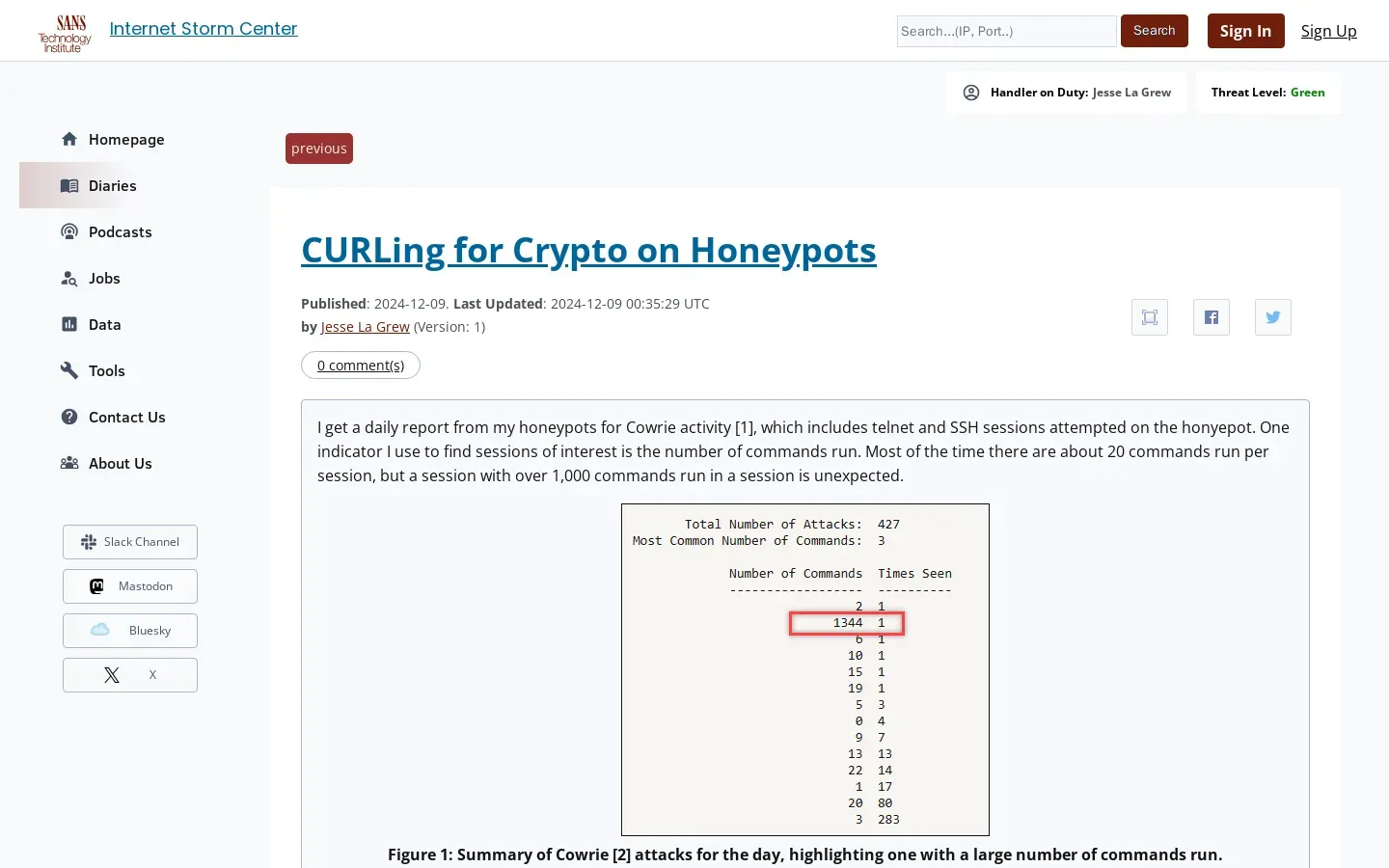
Cybersecurity Strategies for Analyzing Honeypot Activity
/ 5 min read
Quick take - A recent tutorial highlights the use of advanced data analysis tools and continuous monitoring techniques to enhance cybersecurity by improving the analysis of cyber threats and tracking suspicious IP addresses.
Fast Facts
- A recent tutorial emphasizes the use of advanced data analysis tools like JQ and DShield-SIEM to enhance cybersecurity by analyzing cyber threats through raw log data.
- The tutorial outlines two main objectives: effectively employing data analysis tools to visualize command execution patterns and establishing continuous monitoring of suspicious IP addresses.
- Implementing these strategies can significantly improve organizations’ abilities to detect and respond to cyber threats, leading to more informed decision-making and resource allocation.
- Key practices include establishing baselines for normal activity, utilizing automated log analysis tools, and conducting manual reviews of suspicious activities to enhance threat detection.
- Recommended tools for managing honeypot activity include Cowrie for capturing malicious interactions, DShield-SIEM for correlating security incidents, and JQ for processing JSON data from logs.
Enhancing Cybersecurity: Leveraging Data Analysis Tools and Monitoring Techniques
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, staying ahead of potential threats is paramount. A recent tutorial has shed light on innovative strategies to bolster cyber defenses by harnessing advanced data analysis tools and monitoring techniques. This initiative focuses on dissecting raw log data, visualizing command execution patterns, and establishing a continuous monitoring system to track suspicious IP addresses.
Key Objectives in Cyber Threat Analysis
The tutorial outlines two primary objectives aimed at enhancing cybersecurity measures. The first goal emphasizes the effective use of data analysis tools such as JQ and DShield-SIEM. JQ, a powerful command-line JSON processor, allows cybersecurity professionals to parse and manipulate JSON data efficiently. Meanwhile, DShield-SIEM serves as a Security Information and Event Management tool that aids in analyzing raw logs. By employing these tools, professionals can create comprehensive dashboards that visualize command execution patterns, enabling them to correlate activities across multiple honeypots. This correlation is crucial for identifying and understanding the tactics employed by cyber adversaries.
The second objective centers around monitoring ongoing activities associated with specific IP addresses. By systematically tracking and documenting the behavior of these addresses over time, cybersecurity experts can identify new patterns and detect emerging websites of interest related to their initial findings. This proactive approach not only enhances the understanding of threat landscapes but also contributes significantly to the overall effectiveness of incident response strategies.
Implications for Cybersecurity Practices
Implementing these strategies has profound implications for the field of cybersecurity. Utilizing sophisticated data analysis tools and establishing a robust monitoring framework can significantly improve an organization’s ability to detect and respond to cyber threats. The capacity to visualize and correlate data from various sources empowers cybersecurity teams to make informed decisions and allocate resources more effectively.
Moreover, ongoing documentation of suspicious activities can lead to the identification of new threats before they escalate, minimizing potential damage. As cyber threats continue to evolve, adopting these advanced analytical techniques will be vital for maintaining the integrity and security of digital infrastructures.
Essential Steps for Analyzing Cowrie Activity
The tutorial provides a detailed roadmap for analyzing Cowrie activity, highlighting four essential steps:
-
Data Collection: Gathering comprehensive data on Cowrie shell usage is crucial. This includes archaeological findings, historical records, and contemporary usage patterns. Compiling diverse sources helps build a robust understanding of Cowrie shells’ cultural significance across different societies.
-
Contextual Analysis: Placing collected information within its historical and cultural context is vital. Examining how Cowrie shells were used in trade, rituals, and social exchanges provides deeper insights into their role in various communities.
-
Quantitative Assessment: Employing statistical methods to analyze the frequency and distribution of Cowrie shells reveals trends over time and geographic regions that may not be apparent through qualitative analysis alone.
-
Interpretation and Application: Researchers are encouraged to interpret their findings in ways that contribute to broader discussions in anthropology and archaeology, drawing connections to modern economic practices and cultural expressions.
Best Practices for Honeypot Activity Analysis
To enhance understanding and efficiency when analyzing honeypot activity, particularly in the context of Cowrie sessions, consider these best practices:
-
Establish Baselines for Normal Activity: Understanding typical behavior within your honeypot is crucial for quickly identifying anomalies that may indicate malicious activities.
-
Utilize Automated Tools for Log Analysis: Automated log analysis tools streamline the process of sifting through large volumes of data, highlighting patterns and flagging unusual activities for further investigation.
-
Correlate Data Across Multiple Honeypots: Comparing activity across different honeypots helps identify common attack vectors and trends, providing deeper insights into attackers’ tactics.
-
Conduct Manual Reviews of Suspicious Activity: While automation is invaluable, manual reviews offer insights that automated systems might miss, such as context around specific interactions or motivations behind certain behaviors.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
When analyzing honeypot activity, users should be aware of common pitfalls such as failing to set appropriate thresholds for ‘unusual’ behavior or neglecting regular updates to honeypot configurations. Additionally, overlooking the importance of correlating honeypot data with other security logs can hinder a comprehensive view of potential threats.
By being mindful of these pitfalls, users can enhance their ability to detect and respond effectively to potential threats. Implementing a robust monitoring strategy, integrating threat intelligence, and continuously refining detection parameters are critical steps in maximizing honeypots’ effectiveness in identifying malicious activities.
Recommended Tools for Honeypot Management
For those managing honeypot activity, particularly in the context of Cowrie:
-
Cowrie: A widely used honeypot simulating SSH and Telnet services that logs interactions with attackers.
-
DShield-SIEM: Offers a collaborative approach to collecting and analyzing security incidents by integrating with various SIEM systems.
-
JQ: A lightweight command-line JSON processor useful for parsing JSON output generated by Cowrie.
By utilizing these tools, cybersecurity professionals can enhance their understanding of attack vectors and improve defensive strategies against potential threats.