Research Highlights Vulnerabilities in Industrial IoT Devices
/ 4 min read
Quick take - Recent research has introduced automated vulnerability scanning tools aimed at enhancing the security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices by identifying and mitigating potential threats in real-time.
Fast Facts
- Recent research has developed automated vulnerability scanning tools to enhance the security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, addressing their susceptibility to cyberattacks.
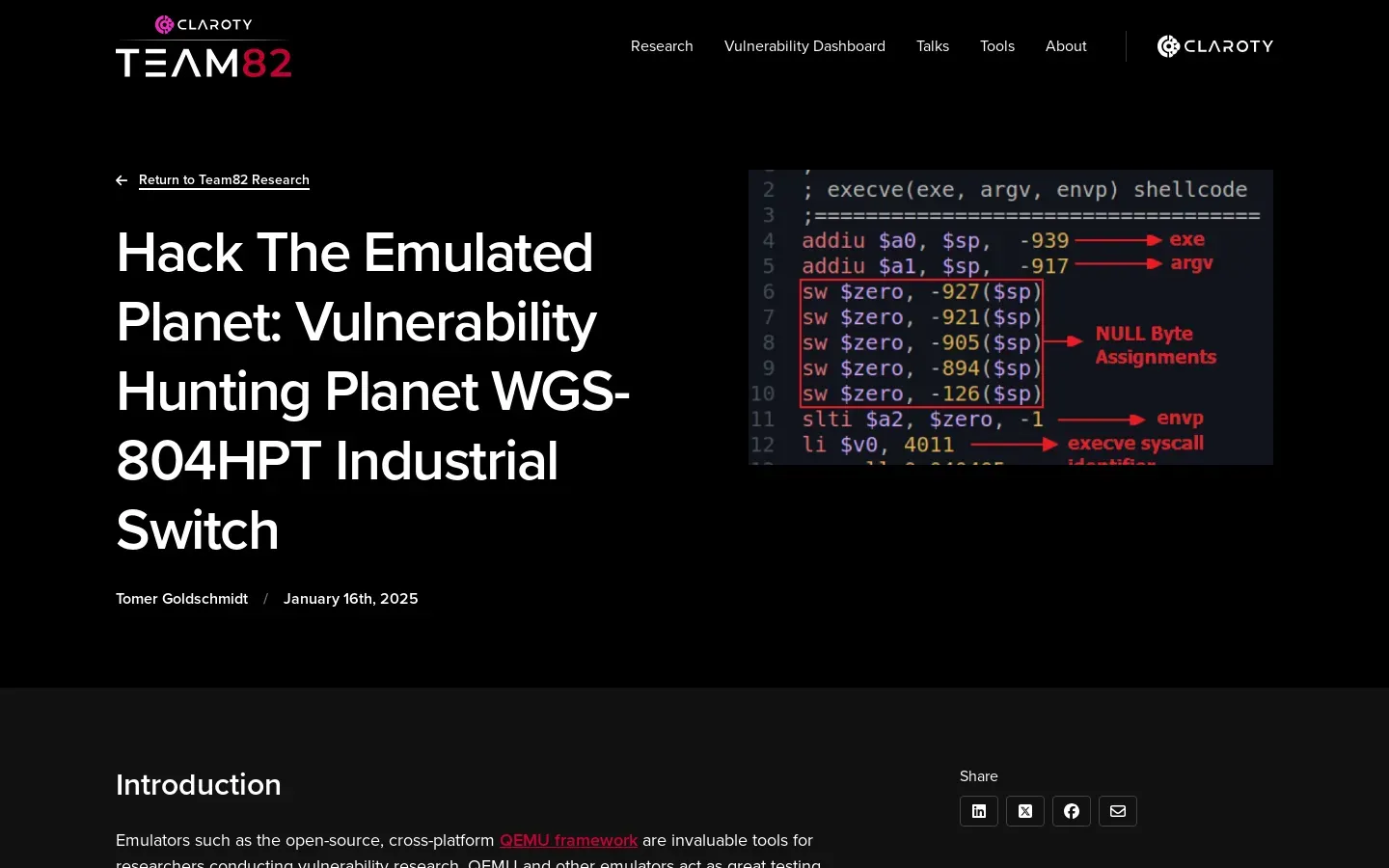
- The study utilized advanced methodologies, including QEMU for emulation and GDB for remote debugging, to facilitate vulnerability discovery and exploit testing in a controlled environment.
- Key findings include improved detection of security flaws and real-time threat simulation, which enhance incident response capabilities for organizations.
- The research emphasizes the importance of training in cybersecurity and collaboration with device manufacturers to integrate security measures from the development stage.
- Future directions focus on refining tools, safe exploit development, and ongoing research to address emerging threats in the evolving IoT landscape.
In an era where the Internet of Things (IoT) has become integral to our daily lives, the cybersecurity landscape is evolving at a dizzying pace. With billions of devices interconnected, the potential attack surface for cybercriminals has expanded exponentially. The research into enhancing cybersecurity measures is not just relevant but critical, especially as we grapple with sophisticated threats that emerge daily. In this context, a series of innovative methodologies and tools have come to the forefront, significantly impacting real-time threat simulation and incident response.
Among the standout advancements is the development of automated vulnerability scanning tools, which streamline the process of identifying security flaws within systems and applications. These tools leverage enhanced vulnerability discovery techniques, enabling security teams to proactively address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers. Coupled with effective training and education initiatives in cybersecurity, organizations can better equip their workforce to recognize and mitigate threats, fostering a culture of vigilance.
As IoT devices proliferate, ensuring their security has become paramount. The research emphasizes an improved security posture for IoT devices, achieved through rigorous testing methodologies and collaboration with device manufacturers for secure development practices. The integration of emulation environments using QEMU (Quick Emulator) allows security professionals to simulate real-world scenarios without risking actual devices. This setup aids in comprehensive vulnerability assessments, enabling more robust defenses against potential breaches.
The significance of chroot environments cannot be overstated either; they provide a sandboxed environment for testing exploits safely. This methodology is crucial for safe exploit development and testing, allowing researchers to analyze vulnerabilities without affecting live systems. Furthermore, the use of Binwalk, a tool designed for firmware analysis, enhances the capabilities of security teams in uncovering weak points in device firmware before they can be targeted.
Despite these strengths, there are notable limitations that call for further investigation. Cross-architecture exploit development remains a challenge, as varying architectures introduce complexity in identifying universally applicable vulnerabilities. This gap highlights an urgent need for advancements in research methodologies that can bridge these differences effectively. Additionally, while automated tools offer efficiency, they must be complemented by rigorous manual testing and validation of exploits to ensure accuracy and effectiveness.
The journey toward heightened cybersecurity resilience does not stop at discovering vulnerabilities; it extends into nurturing collaborative relationships with manufacturers to promote secure coding practices from the ground up. Such partnerships are vital as they lay the groundwork for a more secure future where devices are less likely to fall prey to exploitation.
As we look ahead, the implications of these findings resonate across industries reliant on technology. With cybersecurity threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, organizations must remain vigilant and adaptive. The ongoing evolution of research methods will continue to shape how we approach threat detection and mitigation strategies. Ultimately, fostering a proactive mindset toward cybersecurity will not only enhance individual organizational security postures but contribute to a safer digital ecosystem for all users interacting with IoT technologies. In this fast-paced world where every connection carries risk, staying ahead means investing in knowledge, tools, and collaborative efforts that secure our technological future.